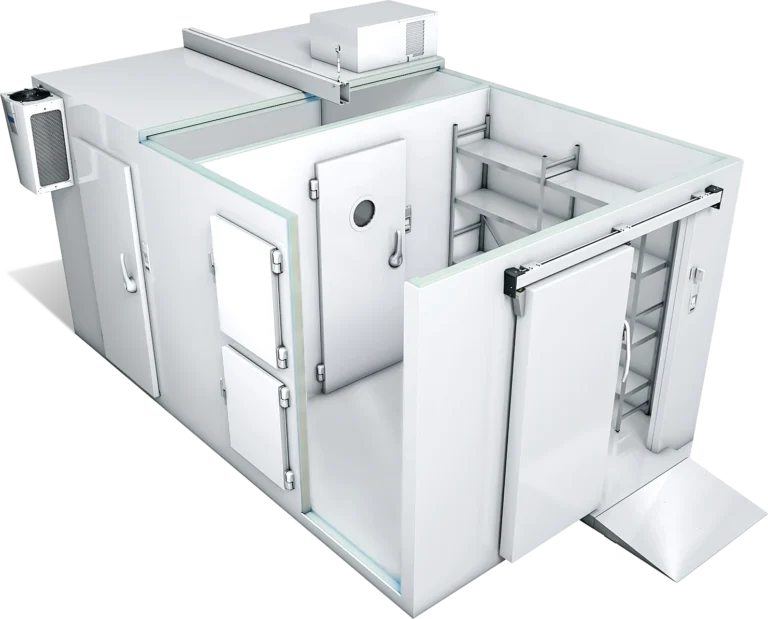

Cold Rooms, As an engineering definition; These are the areas in which a certain temperature is artificially conditioned by transferring the heat inside an area insulated with a Sandwich Panel to another place with the Cooling System. Cold rooms are generally designed to store products in an environment below the outside temperature.Bespoke cold rooms, on the other hand, are designed in the most appropriate way to your project and size and perform this process in the most efficient way.
Cold rooms slows down the chemical and biological processes of the products, and thus deterioration and quality loss are controlled. Through storage in the Cold Room, fruits, vegetables, meat, fish, seafood, etc.It is desired that the products have a longer life without losing quality. Each product must be kept under a certain Temperature, Humidity and Air quality. Depending on the characteristics of each product, the need for temperature, humidity and air varies. At this point, bespoke cold rooms make more sense for your project.In the industry, cold rooms are known by several different names, including:
- Walk-in coolers
- Walk-in freezers
- Walk-in chillers
- Commercial refrigeration units
- Chill rooms
- Refrigerated storage rooms
- Food storage rooms
- Industrial cold storage
- Warehouse refrigeration
The name used may depend on the specific use case and industry, as well as the geographical location. However, these names all refer to the same basic concept of a temperature-controlled room used for storing perishable goods.




Our standard production is 0,5 mm thick sheet on the both surface and 42(+/-2) m3/kg density polyurethane injected interlocking panels between galvanized sheet,CrNi,etc. Corrugated floor panels are the same as wall/ceiling panels with 5 different thicknesses. Corrugated panels have a load bearing capacity of 2000 kg/m2, and optionally, non-slip CrNi or 200 micron PVC coated sheet on plywood can be used on the surface.
| Panel width (mm) | 230 – 530 – 1130 |
| Panel Thickness (mm) | 80 – 100 – 120 – 150 – 200 |
| Panel Density | 40±2 kg/m³ |
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity(EN 13165) | 0,020-0,023 W/mK |
| Thermal Resistance | 2,5 m2 K/W |
| Lock Mechanism | Yes |
| External Sheet Surface Layering Materials | Polyester Painted Galvanised Sheet- PVS – CrNi |
| Colour | RAL 9002 |
| Pattern | Corrugated – Plain |
| Insulator | Polyurethane |
| Sheet thickness (mm) | 0,50 mm |
FAQ:
Bespoke cold rooms take a minimum of 5 working days depending on the dimensions, the capacity of the cooling devices and the complexity of the assembly.
Bespoke cold rooms are priced according to their specific use and size. You can fill out the form to get a quick and accurate price from our customer representatives.
42 ±2 kg/m³ density polyurethane (PUR)
We recommend the use of 80 mm and 100 mm thick panels in cold storage (around +5°C) rooms. We recommend the use of 120 mm thick panels in frosted storage (around -18°C) products. For rooms below these temperatures and for blast freeze rooms, we recommend the use of panels of 150mm and 200mm thickness. As the thickness of the panels increases, the temperature of the room is preserved for a longer time and as a result, the energy costs are reduced to a certain extent. Considering the outside temperatures and such energy costs, panel thicknesses of cold rooms should be carefully selected.
Polyester painted galvanised sheet, Pvc, CrNi (304 quality stainless) are suitable for food safety.
The components we use in our cooling devices are world-renowned brands that have been used for a long time. We share the products we use in our projects with our customers in a transparent manner and we can customize them with components with sufficient capacity according to their choices. Some of the brands we use in our cooling devices are:
Dry food storage should be located nearby the main kitchen and the reception area. Consequently, dry food storage is sometimes neglected when designing food service facilities, and the space reserved for storage is occasionally in an odd spot.
There are a few crucial aspects to consider in the maintenance and control of the dry warehouse, regardless of where it located.
To avoid spoilage and swelling of canned goods, the location needs to be cool and dry. 10°C to 15°C (50°F to 59°F) is the optimal temperature range.
The tank should be simple to maintain clean and pest-free. This means that in order to restrict entry, all wall, ceiling, and floor openings must be secured and sealed.
To facilitate stock rotation, it should be designed such that supplies are simple to arrange and rearrange. The optimal layout places the room’s shelves in the center, where they can be stocked from either side. By sliding the new stock from the opposite side of the rack, you may rotate the stock by pushing the old stock aside. With a “first in first out” (FIFO) idea in stock rotation, this assures that the first products received will also be the first ones used.
The space has to be well-lit.
Shelves must be elevated from the ground by at least 15 cm (6 inches). Items shouldn’t be kept on the ground directly.
Planning the storage of food items should take into account the refrigerator, whether it is a walk-in or a regular upright. To prevent spoilage and decomposition, most fresh foods must be kept in the refrigerator. Always store raw goods beneath cooked or ready-to-eat goods; never store cooked goods above ready-to-eat goods.
Important Control Point
Maintain food at 4 °C (39 °F) or below, the safe range for refrigeration.
To prevent the refrigerator from malfunctioning and exposing food to spoilage, take into account the following:
- Check the refrigerator’s temperature every day. In order to take daily readings, a thermometer should be included in every refrigerator.
- Maintain the functionality of refrigerators.
- Regularly clean the refrigerator. For such quick and simple cleaning, shelves should be shallow and well vented.
- Create and adhere to a schedule to guarantee regular refrigerator cleaning.
All staff using the refrigerator should abide by the following general guidelines:
- Raw foods should be kept above cooked or ready-to-eat foods.
- For refrigerated food, create and adhere to a FIFO system.
- If it’s not absolutely necessary, never refrigerate hot foods. (Unfortunately, there may be variations in how different people define “necessary,” so think about creating rules.)
Dairy products must be stored in the refrigerator at temperatures of 2°C to 4°C (36° to 39°F). Follow these guidelines:
- The fat in dairy products tends to absorb strong odors from the storage surroundings. To reduce the likelihood of this happening, store dairy products in their area in protective coverings.
- Do not store dairy products in a vegetable cooler; a separate refrigerator is much more acceptable.
- Keep the refrigerator clean at all times.
- Rotate dairy products when the fresh product arrives. Dairy products should not be ordered too far in advance of when they will be used. Ideally, such products should be delivered daily.
Most produce is stored in the refrigerator at 2° to 4°C (36° to 39°F) to ensure freshness and prevent rapid deterioration. There are, however, several exceptions, including potatoes and bananas, which should be stored at higher temperatures.
Keep these factors in mind when storing produce:
- Soft fruits should not be stored too long. It is often best to buy soft fruit as you need it, keeping very little on hand.
Unripe fruit can be ripened at storeroom temperatures of 10°C to 15°C (50°F to 59°F). It will ripen much more slowly under refrigerator conditions. - Before storing and when rotating stock, it is important to remove rotting fruit from cases as one piece can affect others. The chain reaction can quickly destroy the quality of a whole case of fruit.
- Be aware of special storage problems. For example, bananas stored in the refrigerator turn black quickly. Bananas should be stored under conditions where the temperature range is 10°C to 15°C (50°F to 59°F).
- The length of time produce can be stored varies widely. For example, hardy vegetables such as carrots and cabbage will last for weeks, while delicate vegetables such as lettuce should be bought as fresh as possible as they do not keep for long.
- Moisture on vegetables tends to soften them, causing rot. Even though in the early stages of rot there is nothing wrong with such vegetables, they can be unattractive to the eye.









